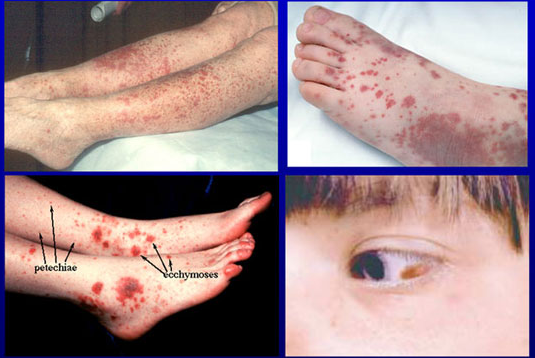
上次跟各位提過瘀青(喜療妥 hirudoid 試用),這次來講一個跟瘀青很類似,但是嚴重很多的疾病:紫斑症。
之前也有跟各位簡單介紹過:
Eltrombopag for the Treatment of Chronic Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
再補充一點資料讓大家熟悉一下:
ITP原本是稱為 Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic PurPur(原因不明的紫斑),不過在1950年,幾位醫師為了找出得病原因,以自己的身體來做實驗,才發現是"免疫抗體"的問題。故改為"Immune",雖仍稱為 ITP。
WJ Harrington 及 JW Hollinsworth 二人,是 Barnes醫院的住院醫師,當時他們都認為 ITP是免疫抗體所產生的疾病,但一直都無法證明
因而兩人決定以一位女病人的血清,輸到自己身上來求證,而Harrington 的血型正好相吻合,所以就先接受輸血..
果然在三小時後,血小板就下降到危險程度,而且還有一次因為有少量腦出血而抽筋(Seizure)全身瘀青,到五天後才完全恢復。
因為Harrington的犧牲成果,使這家醫院全部的血液科醫師,包括主任醫師在內,都用自己的身體來做實驗,這才正式把病名由"原因不明"的"(I)"改成"免疫性"的"(I)"。
以內科來說,正常人的血小板是20萬~40萬/C.C,少於10萬就是不足;
但低於5萬以下,就容易出血;
2、3萬以下,腦及腸的內出血就可能引發危險,必須就醫。
主要因為體內有抗體在對抗血小板,使原本10天壽命變成數小時,身體無法補充就會發生血小板不足的情形。
這種血小板過少症,在女性較多,而且大多是小時候就被察覺。
通常是在一次感冒發燒後就發現容易淤青,而且女孩在初經後,每次月經來時都可能大量出血,經檢查會發現有血小板過少。
也有成年女性發病後,每次月經量比以前多,不以為意,反而沾沾自喜以為這是"健康"的表現,卻不知這是血小板過少的現象。
有紫斑症的母親,在懷孕時會增加不少困擾,因為孕時的母親抗體,會經過胎盤,使胎兒有發病的可能
然而很幸運的是,雖然母親血小板可能低於3萬以下,但在臨床上觀察,真正會對胎兒血小板受到影響的,似乎並不多見。
目前為止,對血小板過少的治療,仍如同10年前一樣,先給予類固醇治療,使血小板維持在5萬至10萬間較佳。
第二步,接受"脾臟"切除
脾是血小板的墳場,因為抗體在血小板上,會使脾臟很容易破壞血小板,多半的病人都會接受這一步。
無論接受何種治療,病人長期都仍會有血小板上上下下變化的困擾,但很慶幸有不少人到了中年後,症狀會緩解許多。
這裡有常見治療方式:
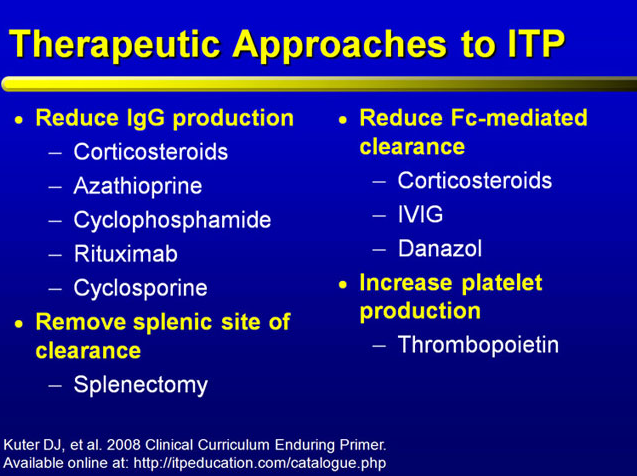
除了類固醇、免疫抑制劑和脾臟切除外,也有使用單株抗體或是IVIG的方式,以及血小板母細胞刺激素 Thrombopoietin (Eltrombopag/promacta)。
所以當您發現有異常大片瘀青,或是經血量過多時,請詢問你的醫師。
看我的文章,當然不會只有藥物介紹這樣簡單,就讓我告訴你一些簡單的藥物使用:
藥物治療:
-
- Immune Suppressants
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are thought to reduce thrombocytopenia by stabilizing vascular integrity, suppressing synthesis of autoantibodies, and decreasing clearance of antibody-coated platelets by WBCs [16].
Oral prednisone is the most commonly used therapeutic agent for ITP.
Intravenous methylprednisolone is the traditional therapeutic agent for ITP patients with platelet counts less than 10,000/microL and life-threatening hemorrhage.
Although additional trials are needed, a Hong Kong study of 125 adults with newly diagnosed ITP found that a 4-day course of oral dexamethasone resulted in a sustained response (platelet count greater than 50,000/microL at 6 months) in 50% of the patients [20]. - Immune Serums
Intravenous Immune Globulin (IVIG)- IVIG works to slow Fc receptor-mediated clearance of antibody-coated platelets by mononuclear, phagocytic cells. [16]
- IVIG is an effective treatment for ITP that, unlike anti-D, can be used in Rh-, Coombs+, or splenectomized patients. However, it is expensive and has some notable side effects, eg, fever and chills during infusion, frequent headache, and increased risk for acute renal failure, especially in volume-depleted patients [16].
Anti-D Immune Globulin- IV anti-D ameliorates thrombocytopenia by coating RBCs, which then competitively inhibit splenic uptake of antibody-bound platelets.[16]
- Anti-D appears equivalent to IVIG in raising the platelet count, is less expensive, and typically has a lower side-effect profile. However, anti-D should not be used in Rh-, Coombs+, or splenectomized patients, and it (rarely) can cause marked hemolytic anemia. [16]
- Thrombopoietin Receptor Agonists
Eltrombopag is indicated for the treatment of thrombocytopenia in patients with chronic immune (idiopathic) thrombocytopenic purpura who have had an insufficient response to corticosteroids, immunoglobulins, or splenectomy. The use of eltrombopag should be limited to patients whose idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura and clinical condition increases the risk of bleeding and should not be used to normalize platelet count. Promacta may be prescribed only by prescribers enrolled in the Promacta Cares Program[21].
Romiplostim is an FDA approved thrombopoietin (TPO) receptor agonist for patients with an insufficient response to corticosteroids, immunoglobulins, or splenectomy whose degree of thrombocytopenia and clinical condition increase the risk for bleeding; it should not be used to normalize platelet counts. Romiplostim may be prescribed and administered only by or under the direction of prescribers enrolled in the Network of Experts Understanding and Supporting Nplate and Patients (Nplate NEXUS) Program Romiplostim stimulates platelet production through binding and activation of the TPO receptor site [15].
- Only patients who are at an increased risk of bleeding due to thrombocytopenia should receive romiplostim. The use of romiplostim is not intended to normalize platelet counts [15].
- Monitoring of CBC, including platelet counts and peripheral blood smears, is required prior to initiation of treatment, throughout therapy, and for at least 2 weeks following discontinuation. Monitor CBC with platelet count and peripheral blood smear weekly until platelet count reaches 50 x 109/L or higher for at least 4 weeks with no dose adjustment. Monitor CBC including platelet count and peripheral blood smear monthly thereafter [15].
- Immune Suppressants
Corticosteroid therapy for idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura[show details and secondary therapies]
Methylprednisolone
Adults: 30 mg/kg IV over 30 minutes (maximum 1 g) once daily for 3 days OR 4 to 6 mg/kg IV in 3 divided doses daily for 3 days
Pediatrics: 30 mg/kg IV over 30 minutes (maximum 1 g) once daily for 3 days OR 4 to 6 mg/kg IV in 3 divided doses daily for 3 days
Prednisone
Adults: 4 to 6 mg/kg/day orally in 3 divided doses for 3 days followed by decremental tapering and discontinuation on day 21
Children: 4 to 6 mg/kg/day orally in 3 divided doses for 3 days followed by decremental tapering and discontinuation on day 21
Immune globulin therapy for idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura[show details and secondary therapies]
Immune Globulin
Adults: 1 g/kg IV daily for 2 days
Pediatrics: 0.4 g/kg IV once OR 1 g/kg IV once daily for 2 days [16]
Rho(D) Immune Globulin
Second line therapy for patients who have had an insufficient response to corticosteroids, immunoglobulins, or splenectomy [21][show details and secondary therapies]
Eltrombopag Olamine
Adults: initial dose, 50 mg (non-east Asian ancestry) OR 25 mg (East Asian ancestry [Chinese, Japanese, Taiwanese, or Korean] or patients with moderate to severe hepatic impairment) once daily on an empty stomach; maintenance dose, after 2 weeks increase dose by 25 mg daily to achieve and maintain a platelet count of 50 x 109/L or more to a maximum of 75 mg/day; if the platelet count fails to increase after 4 weeks at the maximum dose then discontinue; do no administer more than 1 dose within any 24-hour period [21].
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, chronic[show details and secondary therapies]
Romiplostim

Adults: Initial dose 1 mcg/kg subcutaneously once weekly; increase dose weekly by 1 mcg/kg until a platelet count of 50 x 109/L (maximum dose 10 mcg/kg); reduce dose by 1 mcg/kg for platelet count >200 x 109/L for 2 consecutive weeks; do not dose if platelet count is >400 x 109/L, resume at dose reduced by 1 mcg/kg after platelet count falls to <200 x 109/L [15]
最後附上一個nejm的圖解:
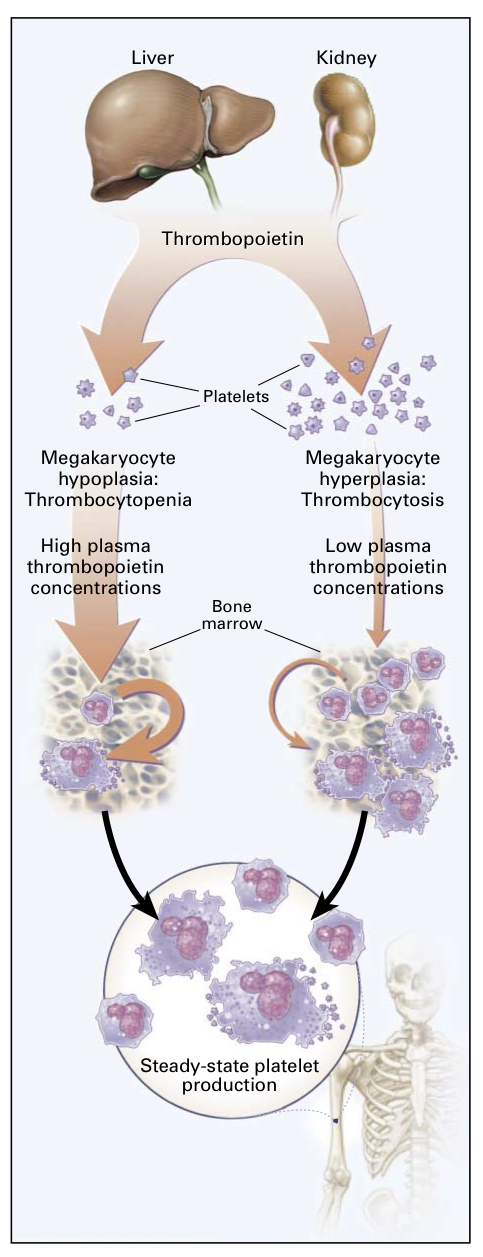
A Model of Thrombopoietin Regulation.
The liver and kidneys produce thrombopoietin constitutively and release it into the circulation. Platelets have recep- tors for thrombopoietin and remove it from plasma. In states of thrombocytopenia (shown in the pathway on the left), little of the released thrombopoietin is metabolized, and the resulting high plasma thrombopoietin concentrations stimulate the hy- poplastic marrow. In addition, marrow stroma produces throm- bopoietin during thrombocytopenia (curved arrow, left). The high plasma thrombopoietin concentrations help restore mega- karyocyte and platelet production. In contrast, during thrombo- cytosis (shown in the pathway on the right), the high numbers of platelets remove most of the thrombopoietin from the circu- lation, and marrow stromal-cell production nearly ceases; as a result, little thrombopoietin is left to act on the numerous megakaryocytes in the marrow (curved arrow, right), allowing it to return to steady-state platelet production. This model is adapted from one proposed by Kuter and Rosenberg.
資料來源:
N Engl J Med 1998; 339:746-754
Micromedex





 留言列表
留言列表
 線上藥物查詢
線上藥物查詢 