NEJM Volume 361:888-898
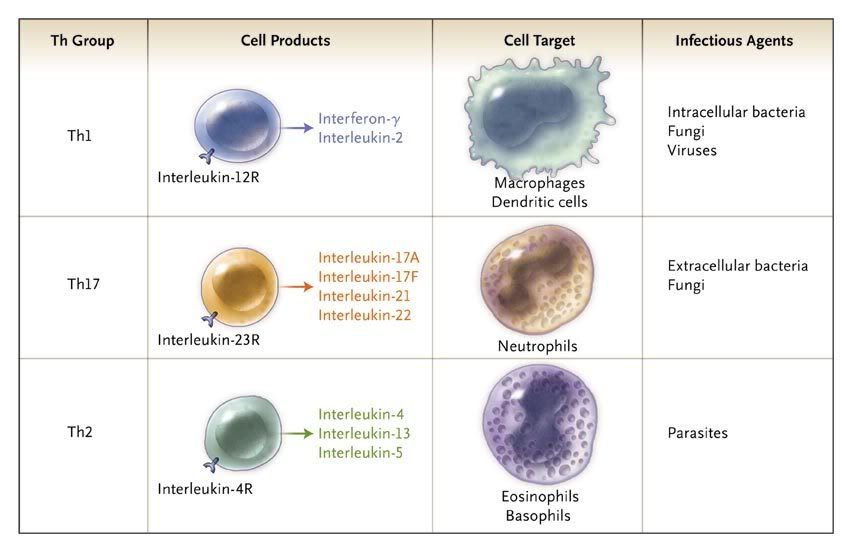
Figure 1. Helper T-Cell (Th) Subgroups and Effector Functions.
The cytokine profile (including key cytokine receptors as denoted by R), the effector cell type that is activated, and the corresponding types of infections are shown for each Th subgroup.
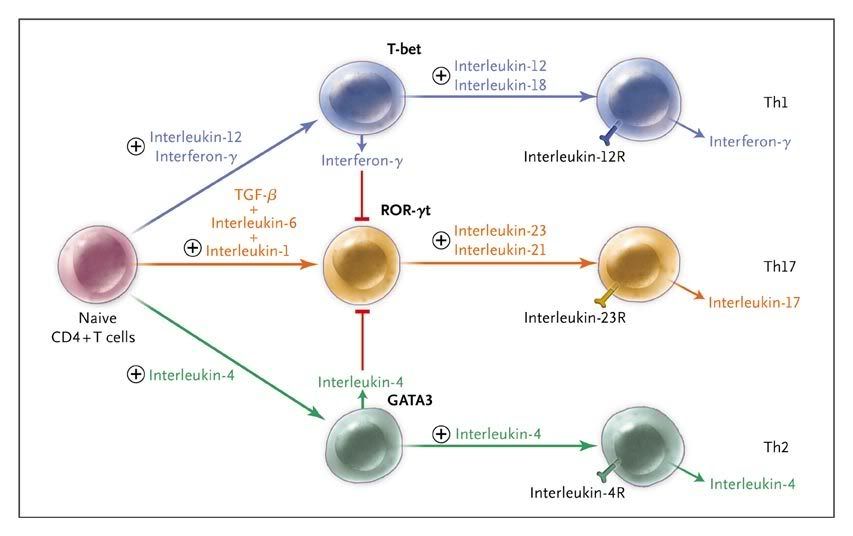
Figure 2. Differentiation of Mouse Th17 Cells.
Naive mouse T cells can differentiate into one of three effector helper T-cell (Th) subgroups. Each pathway is under the control of a different set of cytokines. The Th17 pathway is under the control of transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) plus interleukin-6 and interleukin-1 or TGF-β plus interleukin-21 followed by interleukin-23. This pathway is inhibited by interferon-γ and interleukin-4. The transcription factor (T-bet, ROR-γt, or GATA3) characteristic of each pathway is shown. R denotes receptor.
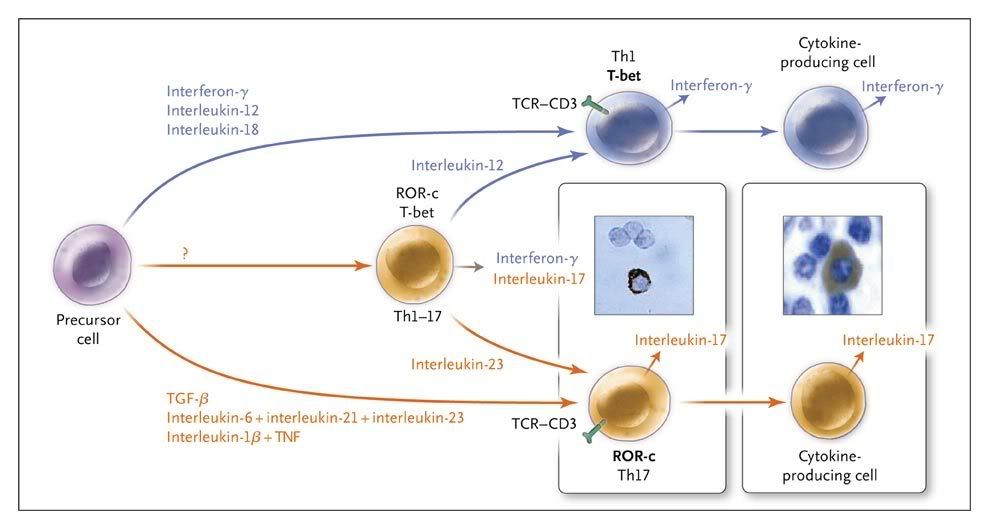
Figure 3. Differentiation of Human Th17 Cells.
Key cytokines for the development of human Th17 cells are transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) plus interleukin-6, interleukin-21, and the inflammatory cytokine interleukin-1, followed by interleukin-23. In addition to the classic Th1 and Th17 subgroups, a mixed Th1–Th17 subgroup has been identified, which expresses both T-bet and ROR-c. In inflammatory tissues, fully differentiated cytokine-producing cells have been observed. The micrographs show immunohistochemical staining of the cytoplasm for antibodies against interleukin-17 (brown) in human blood CD4+ T cells activated in vitro for 24 hours and a plasma-cell–like cell in a section of rheumatoid synovium. These cell have lost their T-cell receptor (TCR) and the CD3 complex. TNF denotes tumor necrosis factor.
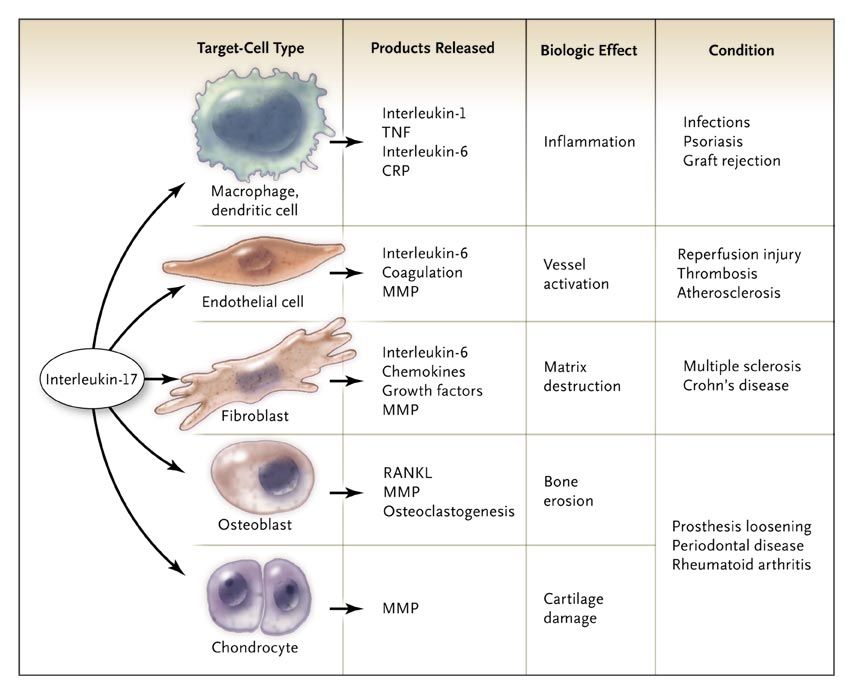
Figure 4. Effects of Interleukin-17 on Cell Functions and Its Role in the Pathophysiology of Diseases.
For each key effect of interleukin-17, the target-cell type involved and the products released in response to interleukin-17 are shown. Each biologic effect is linked to examples of conditions in which an association with the presence of interleukin-17 has been observed. CRP denotes C-reactive protein, MMP matrix metalloproteinase, RANKL receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand, and TNF tumor necrosis factor.





 留言列表
留言列表
 線上藥物查詢
線上藥物查詢 