圖一:
Evolution of Multiple Myeloma and Interactions between Plasma Cells and the Bone Marrow Microenvironment.
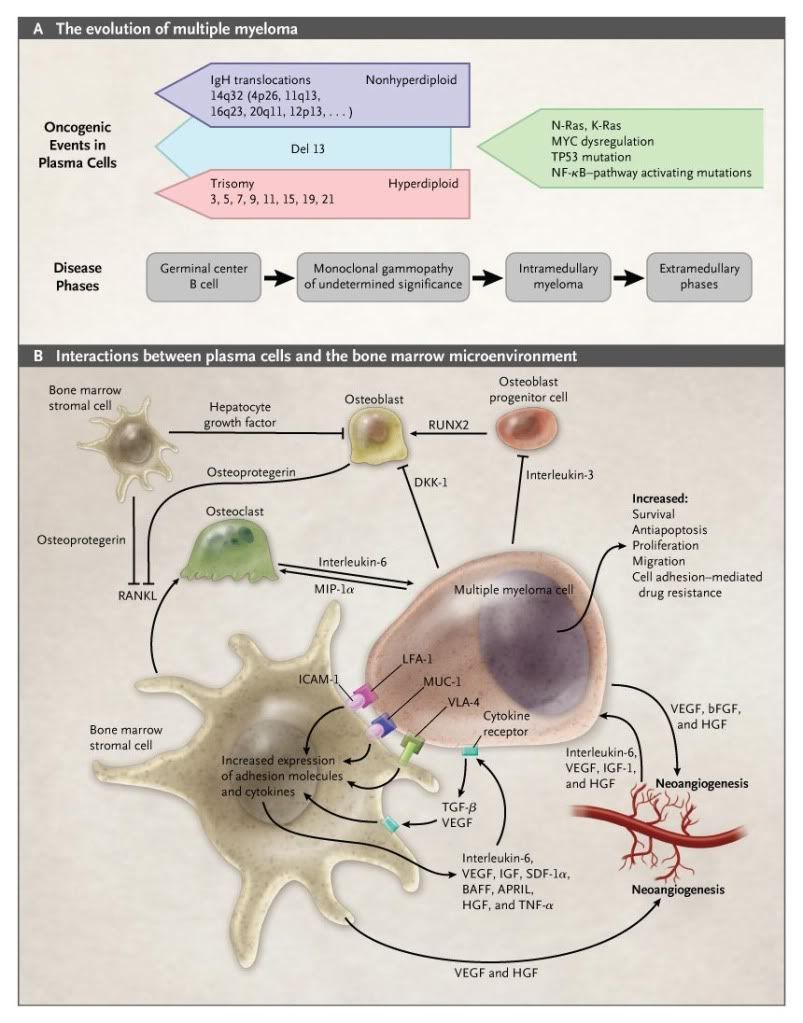
Panel A shows the clinical evolution of multiple myeloma, which typically proceeds from a clonal proliferation of plasma cells, termed monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS), through intramedullary myeloma to extramedullary disease. This sequence is accompanied by progressive genetic changes, which include chromosomal changes (translocations, deletions, and trisomy), followed in later stages by oncogene mutations. Panel B shows the adhesion of myeloma cells to bone marrow stromal cells, which is mediated by specific interactions between cell-surface molecules, including the interaction between intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) and leukocyte-function–associated antigen 1 (LFA-1) and between very late antigen 4 (VLA-4) and vascular-cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1). These interactions trigger transcription and secretion of cytokines. Bone marrow stromal cells secrete interleukin-6, which stimulates myeloma-cell growth, proliferation, and migration and confers resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs. Myeloma cells also secrete cytokines, including tumor growth factor β, which further up-regulates interleukin-6 and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which stimulates neoangiogenesis. In addition, RANKL, which is produced by bone marrow stromal cells, and macrophage inflammatory protein 1 (MIP-1
(MIP-1 ), which is produced by myeloma cells, stimulate osteoclast proliferation, whereas osteoblast proliferation is inhibited by interleukin-3, dickkopf homologue 1 (DKK-1), and hepatocyte growth factor (HGF). APRIL denotes a proliferation-inducing ligand, BAFF blockade of B-cell–activating factor, bFGF basic fibroblast growth factor, IGF insulin-like growth factor, MUC-1 mucin type 1, NF-
), which is produced by myeloma cells, stimulate osteoclast proliferation, whereas osteoblast proliferation is inhibited by interleukin-3, dickkopf homologue 1 (DKK-1), and hepatocyte growth factor (HGF). APRIL denotes a proliferation-inducing ligand, BAFF blockade of B-cell–activating factor, bFGF basic fibroblast growth factor, IGF insulin-like growth factor, MUC-1 mucin type 1, NF- B nuclear factor kappa B, RUNX2 runt-related transcription factor 2, SDF-1
B nuclear factor kappa B, RUNX2 runt-related transcription factor 2, SDF-1 stromal-cell–derived factor 1
stromal-cell–derived factor 1 , TGF-β transforming growth factor β, and TNF-
, TGF-β transforming growth factor β, and TNF- tumor necrosis factor
tumor necrosis factor  . Data are from Hideshima et al. and Hideshima et al.
. Data are from Hideshima et al. and Hideshima et al.
圖二:
Homing of Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cells to Bone Marrow.
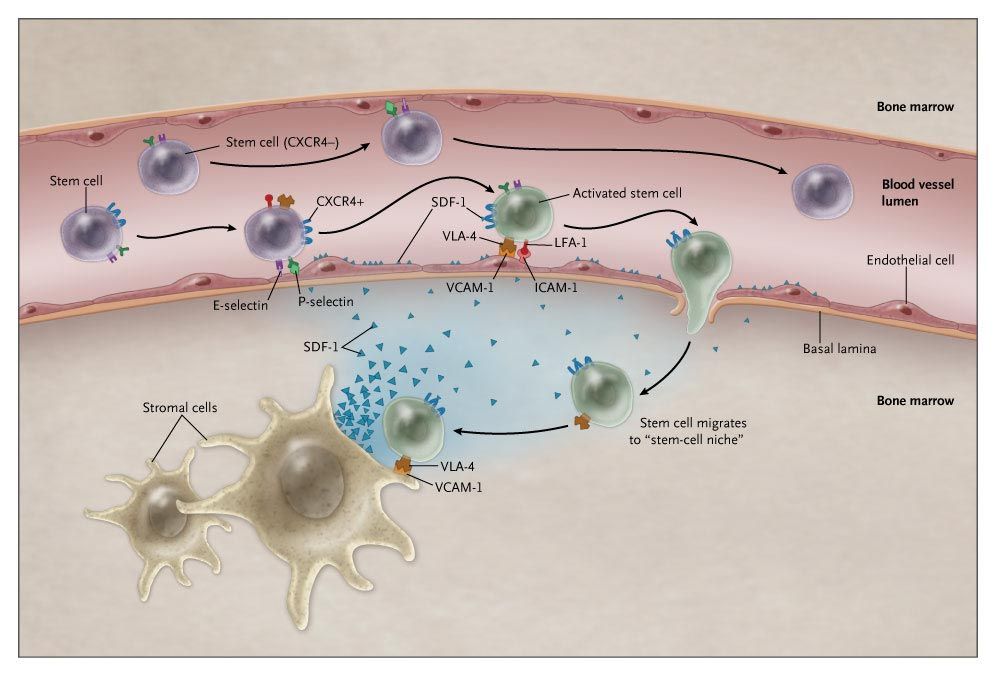
Hematopoietic stem cells express the chemokine receptor CXCR4, whereas bone marrow stromal cells express chemokine stromal cell–derived factor 1 (SDF-1). After stem cells are infused into a recipient, SDF-1 activates CXCR4-positive stem cells, stimulating adhesion to endothelial cells through interaction between intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) and leukocyte-function–associated antigen 1 (LFA-1) and between very late antigen 4 (VLA-4) and vascular-cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1). These stem cells then extravasate into the bone marrow stroma and adhere to stromal cells through similar adhesion interactions between cells. Data are from Peled et al.
資料來源:NEJM Volume 360:2645-2654





 留言列表
留言列表
 線上藥物查詢
線上藥物查詢 