
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved vismodegib (Erivedge) for the treatment of an advanced form of basal cell carcinoma (BCC). The indication is for BCC that has metastasized or relapsed after treatment with surgery, or for patients who are not candidates for surgery or radiation.
This is the first FDA-approved drug for use in the advanced forms of the most common skin cancer.
"Today's approval provides a new treatment for people with advanced basal cell carcinoma who, until now, had no approved medicines to help shrink disfiguring or potentially life-threatening lesions," said Hal Barron, MD, chief medical officer and head of global product development at Genentech, the manufacturer of vismodegib.
"We are pleased that in the past 6 months we have been able to provide 2 new medicines for different types of advanced skin cancer to people who previously had few or no treatment options," said Dr. Barron in a statement.
BCC is usually curable if the lesions are restricted to a small area of the skin. However, in rare cases, the lesions can become disfiguring, invade surrounding tissue, or metastasize. In these instances of advanced BCC, the disease cannot be effectively treated with surgery or radiation — the standard treatments.
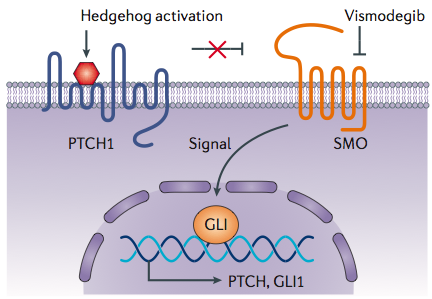
Vismodegib is an oral drug that is designed to selectively inhibit abnormal signaling in the Hedgehog pathway, which is an underlying molecular driver of BCC. It binds to and inhibits Smoothened, a transmembrane protein involved in Hedgehog signal transduction.
The agent was reviewed under the FDA's priority review program, which provides for an expedited 6-month review of drugs that might offer major advances in treatment. The drug was approved ahead of the prescription user fee goal date, which was March 8, 2012.
The safety and effectiveness of vismodegib was evaluated in a single multicenter clinical study that involved 96 patients with locally advanced or metastatic BCC. Of this group, 21% carried a diagnosis of Gorlin syndrome. The primary end point was objective response rate of the cancerous lesions after treatment. In patients with metastatic disease, 30% achieved a partial response; in patients with locally advanced disease, 43% achieved a complete or partial response.
The most common adverse reactions (incidence of 10% or more) were muscle spasms, alopecia, dysgeusia, weight loss, fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, decreased appetite, constipation, arthralgias, vomiting, and ageusia.
Vismodegib has been approved with a boxed warning stating that use of this drug can result in embryo-fetal death or severe birth defects. Pregnancy status must be verified prior to initiation of treatment, and both male and female patients need to be advised of these risks. Women need to be advised of the need for contraception and men of the potential risk for vismodegib exposure through semen.
"Our understanding of molecular pathways involved in cancer, such as the Hedgehog pathway, has enabled the development of targeted drugs for specific diseases," said Richard Pazdur, MD, director of the Office of Hematology and Oncology Products at the FDA's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, in a statement. "This approach is becoming more common and will potentially allow cancer drugs to be developed more quickly. This is important for patients, who will have access to more effective therapies with potentially fewer side effects."
Roche and Genentech are currently evaluating vismodegib in a phase 2 trial for patients with operable forms of BCC.





 留言列表
留言列表
 線上藥物查詢
線上藥物查詢 