其實仔細找一下就會發現,這些證據強度的分類還有因為不同國家或是不同組織有不同的分法,所以簡單選一些常見的給大家參考:
|
Grade
|
US Preventive Task Force
|
NHS R&D Center for EBM
|
|
|
A
|
This is good evidence to support the Recommendation
|
1a
|
SR of RCT
(with narrow confidence interval)
|
|
1b
|
individual RCT
(with narrow confidence interval)
|
||
|
1c
|
All-or-none studies
|
||
|
B
|
There is fair evidence to support the Recommendation
|
2a
|
SR of cohort studies
( with homogeneity )
|
|
2b
|
individual cohort study or low-quality RCT(<80% follow up)
|
||
|
2c
|
outcome research;Ecological studies
|
||
|
3a
|
SR of case-control study
|
||
|
3b
|
individual case-control study
|
||
|
C
|
There is insufficient evidence for or
against, but recommendation may be made on other grounds
|
Case series and poor quality cohort/case-control
Studies
|
|
|
D
|
There is fair evidence to exclude the Recommendation
|
Expert opinion without explicit critical appraisal, or
based on bench research
|
|
|
E
|
There is good evidence to exclude the recommendation
|
||
|
Grade
|
US Preventive Task Force
|
NHS R&D Center for EBM
|
|
|
A
|
This is good evidence to support the Recommendation
|
1a
|
整體隨意控制試驗(Total RCT)的系統性回顧(Systematic review)
|
|
1b
|
個別隨意控制試驗(Individual RCT)
|
||
|
1c
|
All-or-none studies
|
||
|
B
|
There is fair evidence to support the Recommendation
|
2a
|
整體相關病人研究(Cohort study)的系統性回顧
|
|
2b
|
個別相關病人研究
|
||
|
2c
|
指標結果(Outcome)研究
|
||
|
3a
|
整體個案控制研究(Case-control study)的系統性回顧,
|
||
|
3b
|
個別個案控制研究
|
||
|
C
|
There is insufficient evidence for or
against, but recommendation may be made on other grounds
|
個案系列研究
|
|
|
D
|
There is fair evidence to exclude the Recommendation
|
未根據嚴格判斷的,或只根據生理或實驗研究的專家意見
|
|
|
E
|
There is good evidence to exclude the recommendation
|
||
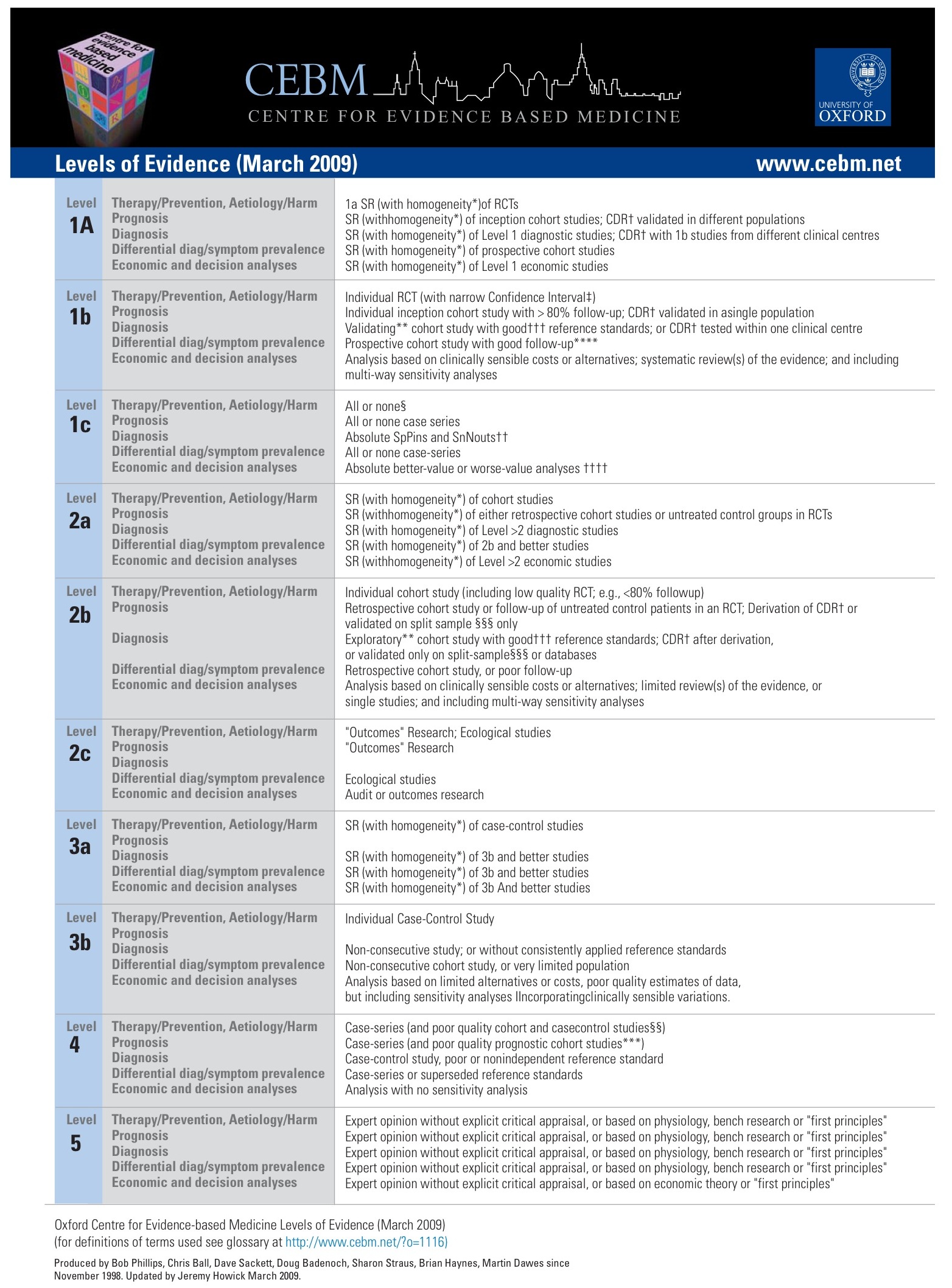
Oxford Centre for Evidence-based Medicine Levels of Evidence (May 2001)
|
Level |
Therapy/Prevention, Aetiology/Harm |
Prognosis |
Diagnosis |
Differential diagnosis/symptom prevalence study |
Economic and decision analyses |
|
1a |
SR (withhomogeneity*) of RCTs |
SR (withhomogeneity*) of inception cohort studies;CDR†validated in different populations |
SR (withhomogeneity*) of Level 1 diagnostic studies; CDR†with 1b studies from different clinical centres |
SR (withhomogeneity*) of prospective cohort studies |
SR (withhomogeneity*) of Level 1 economic studies |
|
1b |
Individual RCT (with narrow Confidence Interval‡) |
Individual inception cohort study with > 80% follow-up;CDR†validated in a single population |
Validating** cohort study withgood††† reference standards; orCDR† tested within one clinical centre |
Prospective cohort study with good follow-up**** |
Analysis based on clinically sensible costs or alternatives; systematic review(s) of the evidence; and including multi-way sensitivity analyses |
|
1c |
All or none case-series |
All or none case-series |
Absolute better-value or worse-value analyses †††† |
||
|
2a |
SR (withhomogeneity*) of cohort studies |
SR (withhomogeneity*) of either retrospective cohort studies or untreated control groups in RCTs |
SR (withhomogeneity*) of Level >2 diagnostic studies |
SR (withhomogeneity*) of 2b and better studies |
SR (withhomogeneity*) of Level >2 economic studies |
|
2b |
Individual cohort study (including low quality RCT; e.g., <80% follow-up) |
Retrospective cohort study or follow-up of untreated control patients in an RCT; Derivation ofCDR† or validated on split-sample§§§ only |
Exploratory** cohort study withgood†††reference standards; CDR†after derivation, or validated only on split-sample§§§ or databases |
Retrospective cohort study, or poor follow-up |
Analysis based on clinically sensible costs or alternatives; limited review(s) of the evidence, or single studies; and including multi-way sensitivity analyses |
|
2c |
"Outcomes" Research; Ecological studies |
"Outcomes" Research |
|
Ecological studies |
Audit or outcomes research |
|
3a |
SR (withhomogeneity*) of case-control studies |
|
SR (withhomogeneity*) of 3b and better studies |
SR (withhomogeneity*) of 3b and better studies |
SR (withhomogeneity*) of 3b and better studies |
|
3b |
Individual Case-Control Study |
|
Non-consecutive study; or without consistently applied reference standards |
Non-consecutive cohort study, or very limited population |
Analysis based on limited alternatives or costs, poor quality estimates of data, but including sensitivity analyses incorporating clinically sensible variations. |
|
4 |
Case-series (andpoor quality cohort and case-control studies§§) |
Case-series (and poor quality prognostic cohort studies***) |
Case-control study, poor or non-independent reference standard |
Case-series or superseded reference standards |
Analysis with no sensitivity analysis |
|
5 |
Expert opinion without explicit critical appraisal, or based on physiology, bench research or "first principles" |
Expert opinion without explicit critical appraisal, or based on physiology, bench research or "first principles" |
Expert opinion without explicit critical appraisal, or based on physiology, bench research or "first principles" |
Expert opinion without explicit critical appraisal, or based on physiology, bench research or "first principles" |
Expert opinion without explicit critical appraisal, or based on economic theory or "first principles" |
Produced by Bob Phillips, Chris Ball, Dave Sackett, Doug Badenoch, Sharon Straus, Brian Haynes, Martin Dawes since November 1998.
CEBM有提供2009版的OXFORD:
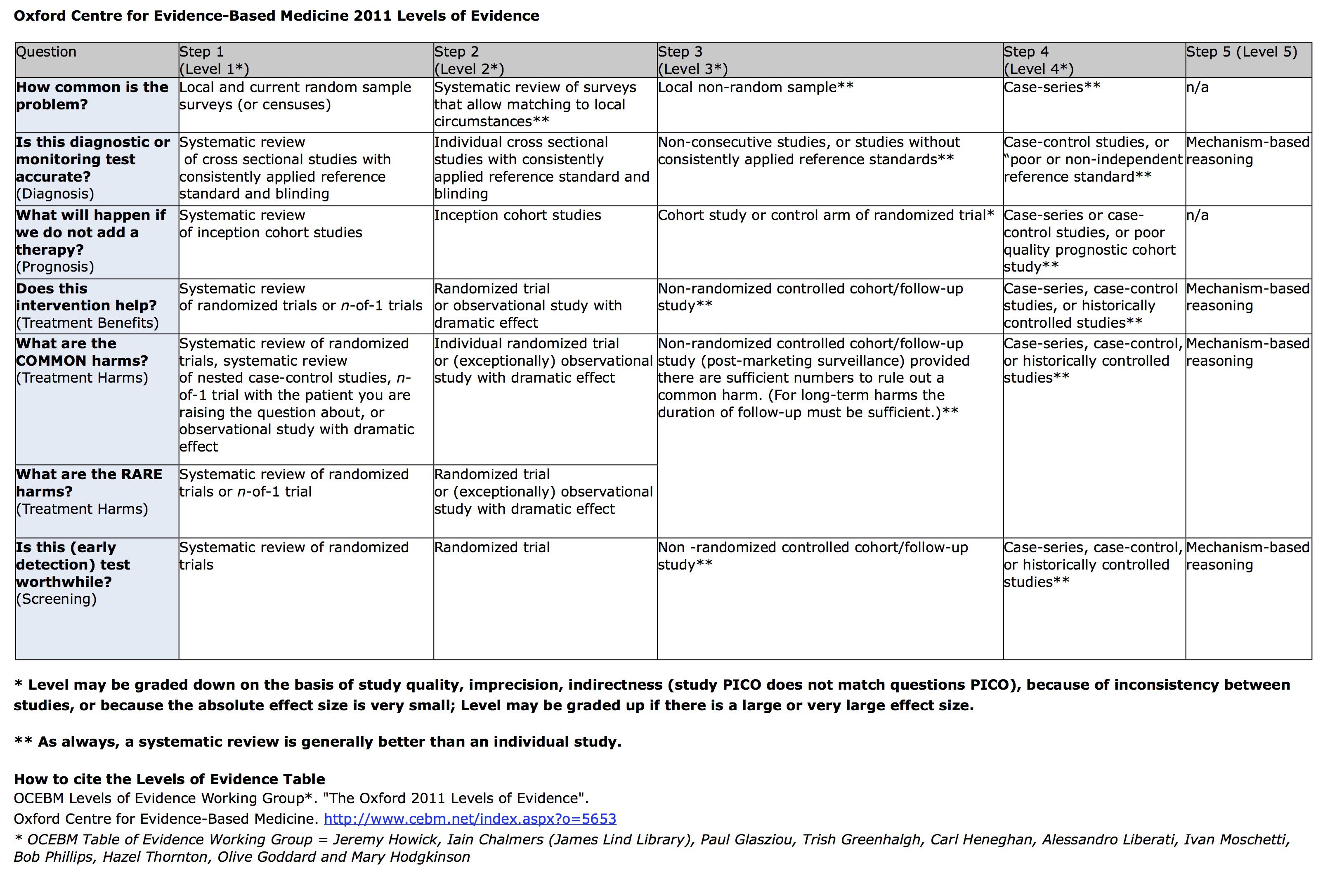
2011版的:
在第二屆American Heart Association (AHA)International Evidence Evaluation Conference 以及the international Guidelines 2000 Conference on CPR and ECC,國際間專家的參與,大幅改變了未來的急救準則。未來的急救準則,必需要有國際性的實證醫學研究資料(evidence-based medicine)為基礎,才能達到應有的正確性及可信度。
|
證據等級
|
說明
|
|
Class I
|
表示在人體實驗上證明良好,確定有效之證據,並至少有一證據是前瞻性、隨機、控制下、正面效果的臨床試驗。
|
|
Class IIa
|
表示在人體實驗上是安全、有效。許多專家認為標示Class Ⅱa 的指引,非常值得推薦採用。
|
|
Class IIb
|
指證據力不及Ⅱa,但對人體無害。許多專家認為標示Ⅱb 之指引為可接受之替代方案。
|
|
尚待決定
|
證據不足以支持建議為臨床使用。通常這些指引尚在臨床嘗試階段,需要進一步再收集資料判斷。
|
|
Class III
|
表示沒有效用,但可能有害,因此不被接受。
|
- Level I: Evidence obtained from at least one properly designed randomized controlled trial.
- Level II-1: Evidence obtained from well-designed controlled trials without randomization.
- Level II-2: Evidence obtained from well-designed cohort or case-control analytic studies, preferably from more than one center or research group.
- Level II-3: Evidence obtained from multiple time series with or without the intervention. Dramatic results in uncontrolled trials might also be regarded as this type of evidence.
- Level III: Opinions of respected authorities, based on clinical experience, descriptive studies, or reports of expert committees.
- Level A: Consistent Randomised Controlled Clinical Trial, cohort study, all or none (see note below),clinical decision rule validated in different populations.
- Level B: Consistent Retrospective Cohort, Exploratory Cohort, Ecological Study, Outcomes Research, case-control study; or extrapolations from level A studies.
- Level C: Case-series study or extrapolations from level B studies.
- Level D: Expert opinion without explicit critical appraisal, or based on physiology, bench research or first principles.
- Level A: Good scientific evidence suggests that the benefits of the clinical service substantially outweighs the potential risks. Clinicians should discuss the service with eligible patients.
- Level B: At least fair scientific evidence suggests that the benefits of the clinical service outweighs the potential risks. Clinicians should discuss the service with eligible patients.
- Level C: At least fair scientific evidence suggests that there are benefits provided by the clinical service, but the balance between benefits and risks are too close for making general recommendations. Clinicians need not offer it unless there are individual considerations.
- Level D: At least fair scientific evidence suggests that the risks of the clinical service outweighs potential benefits. Clinicians should not routinely offer the service to asymptomatic patients.
- Level I: Scientific evidence is lacking, of poor quality, or conflicting, such that the risk versus benefit balance cannot be assessed. Clinicians should help patients understand the uncertainty surrounding the clinical service.
Quality of Evidence





 留言列表
留言列表
 線上藥物查詢
線上藥物查詢 