
SAN ANTONIO, Texas — Omalizumab (Xolair, Roche, Genentech, Novartis) appears to be safe and effective in the treatment of chronic idiopathic urticaria that is refractory to antihistamines, according to new phase 3 clinical trial results.

SAN ANTONIO, Texas — Omalizumab (Xolair, Roche, Genentech, Novartis) appears to be safe and effective in the treatment of chronic idiopathic urticaria that is refractory to antihistamines, according to new phase 3 clinical trial results.

Primary care physicians are up in arms about the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10), and no doubt the new diagnosis system is complex and highly specific. But although the transition will create some upheaval and loss of time, in the long run ICD-10 may bring financial and clinical benefits for primary care doctors.

A new antibiotic, tedizolid phosphate, appears to be a reasonable alternative to linezolid for the treatment of acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI): A short (6-day) course of tedizolid phosphate was as effective as a 10-day course of linezolid with regard to both early and sustained clinical responses.

What is the significance of reports of adverse cardiac outcomes associated with calcium supplements?
Response from Darrell Hulisz, PharmD
Associate Professor, Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine; Clinical Specialist in Family Medicine, University Hospitals, Case Medical Center, Cleveland, Ohio
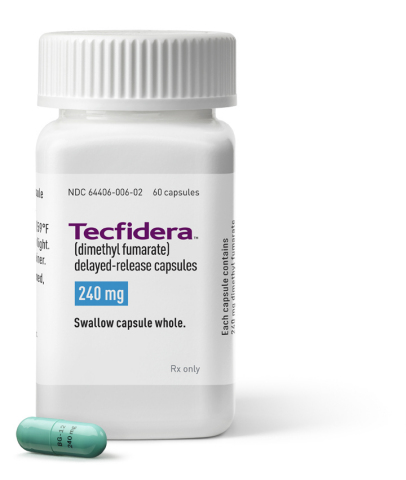
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved dimethyl fumarate (Tecfidera, Biogen Idec) for the treatment of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (MS).

The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) today announced that it has halted all pediatric clinical trials of cinacalcet (Sensipar, Amgen), a calcium-lowering drug, after the recent death of a 14-year-old patient in a study.
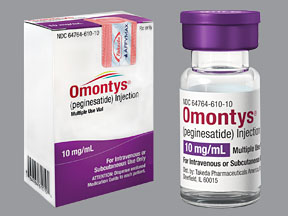
The anemia drug peginesatide (Omontys, Affymax and Takeda Pharmaceuticals) has been voluntarily recalled by the manufacturers after reports of anaphylaxis leading to 3 deaths, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced today.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has expanded the approved use of deferasirox (Exjade, Novartis) to treat patients aged 10 years and older with chronic iron overload due to nontransfusion-dependent thalassemia (NTDT), the agency announced today.

Current therapy for asthma with inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting inhaled β2-agonists is highly effective, safe, and relatively inexpensive, but many patients remain poorly controlled. Most advances have been through improving these drug classes and a major developmental hurdle is to improve existing drug classes. Major unmet needs include better treatment of severe asthma (which has some similarity to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease), as well as curative therapies for mild to moderate asthma that do not result in the return of symptoms when the treatment is stopped. Several new treatments are in development, but many are specific, targeting a single mediator or receptor, and are unlikely to have a major clinical impact, although they may be effective in specific asthma phenotypes (endotypes). Drugs with more widespread effects, such as kinase inhibitors, may be more effective but have a greater risk of side effects so inhaled delivery may be needed. Several new treatments target the underlying allergic/immune process and would treat concomitant allergic diseases. Improved immunotherapy approaches have the potential for disease modification, although prospects for a cure are currently remote.
LONDON — The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has finalized a review of recently published information on the cardiovascular safety of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and concludes that the latest evidence shows a consistent but small increase in the risk of cardiovascular side effects with diclofenac compared with other NSAIDs [1]. The risk with diclofenac is "similar to the risks of COX-2 inhibitors," it states.
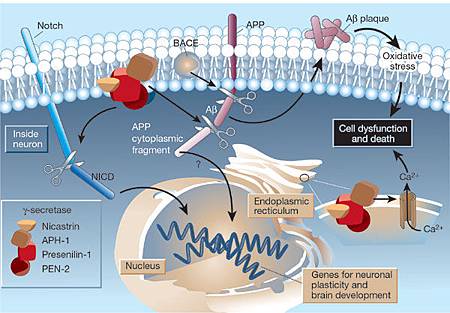
Investigators have selected the first drugs to be evaluated in an Alzheimer's disease (AD) prevention trial.
Doernberg SB, Winston LG, Deck DH, Chambers HF
Clin Infect Dis. 2012;55:615-620.
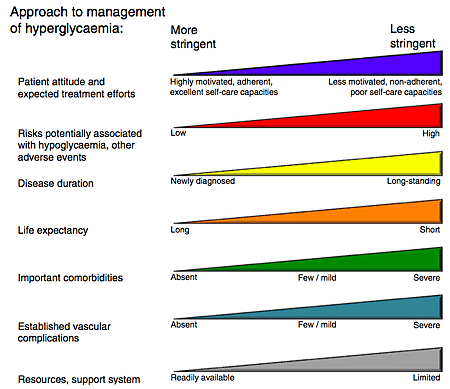
A new position statement for the treatment of type 2 diabetes takes an approach much more focused on the individual patient compared with the "one number fits all" target of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) used up to now.

Prescribers and patients often voice concerns about the safety and efficacy of generic drugs that are substituted for brand-name drug products. Love 'em or hate 'em, they are with us to stay. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approves a generic substitute if it has proven to be "identical, or bioequivalent, to a brand-name drug in dosage form, safety, strength, route of administration, quality, performance characteristics, and intended use."[1]
Question:
What are the maximum doses of potassium, calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium that can be taken orally without significant adverse effect and with maximum clinical effect?
口服鉀、鈣、磷、鎂的建議最大有效劑量(沒有明顯副作用)是多少呢?
Response from Jenny A. Van Amburgh, PharmD, CDE
Assistant Dean of Academic Affairs and Associate Clinical Professor, School of Pharmacy, Northeastern University; Director, Clinical Pharmacy Team and Residency Program Director, Harbor Health Services, Inc., Boston, Massachusetts

According to the current study by Jneid and colleagues, new evidence is available on the management of unstable angina. This report replaces the 2007 American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Unstable Angina/Non–ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction (UA/NSTEMI) that were updated by the 2011 guidelines.
An indirect comparison of the new oral anticoagulant drugs, with all the caveats that such comparisons entail, suggests there is no profound difference between apixaban (Eliquis, Pfizer/Bristol-Myers Squibb), rivaroxaban (Xarelto, Bayer/Johnson & Johnson), or dabigatran (Pradaxa, Boehringer Ingelheim) in terms of efficacy [1]. The higher dose of dabigatran, 150 mg, was superior to rivaroxaban in terms of lowering the risk of stroke or systemic embolism, while the risk of major bleeding was significantly lower with dabigatran 110 mg or apixaban when compared with rivaroxaban.